Sofia API Reference
- Package Index
- Class Index
- Packages
- sofia.app
- sofia.content
- sofia.data
-
sofia.graphics
- Interfaces
- Joint
- PropertyTransformer
- Classes
- AbstractJoint
- Anchor
- Color
- CoordinateSystem
- DirectionalPad
- DistanceJoint
- ElasticInInterpolator
- ElasticInOutInterpolator
- ElasticOutInterpolator
- FillableShape
- FillableShape.Animator
- Geometry
- Image
- LineShape
- MotionStep
- OvalShape
- PointAndAnchor
- Polygon
- PolygonShape
- Predicate
- RectangleShape
- RevoluteJoint
- Shape
- Shape.Animator
- Shape.Filter
- ShapeField
- ShapeFilter
- ShapeSet
- ShapeView
- SizeF
- StrokedShape
- StrokedShape.Animator
- TextShape
- TextShape.Animator
- Timings
- ViewEdges
- ZIndexComparator
- Enums
- RepeatMode
- ShapeMotion
- sofia.util
- sofia.view
- sofia.widget
Inheritance
 Known Direct Subclasses Known Direct Subclasses
| |||||||||||||||
 Known Indirect Subclasses Known Indirect Subclasses
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Class Overview
The base class for all types of shapes that can be drawn on a
ShapeView. This class maintains all of the properties that are
common to every type of shape, such as its bounds (position and size on the
canvas), visibility, color (though some subclasses define multiple kinds of
colors), and rotation. Animation support is also provided through this
class.
Summary
| Nested Classes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| class | Shape.Animator<AnimatorType extends Animator<AnimatorType>> | Provides animation support for shapes. | |||||||||
| class | Shape.Filter<FilterType extends Animator<FilterType>> | ||||||||||
| Public Constructors | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Shape()
Creates a new shape.
| ||||||||||
| Public Methods | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
void
|
addOther(Shape newShape)
Add another shape to the same view (or composite shape) containing this
shape.
| ||||||||||
Animator<?>
|
animate(long duration)
Gets an animator object that lets the user animate properties of the receiving shape. | ||||||||||
void
|
applyLinearImpulse(float x, float y)
TODO document
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
contains(PointF point)
Gets a value indicating whether the specified pixel location is
contained in the receiver.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
contains(float x, float y)
Gets a value indicating whether the specified pixel location is contained in the receiver. | ||||||||||
abstract
void
|
draw(Canvas canvas)
Subclasses must implement this method to define how the shape is to be
drawn on the canvas.
| ||||||||||
ViewEdges
|
extendsOutside(RectF bounds)
Determine whether any part of this shape extends outside the given
rectangle.
| ||||||||||
int
|
getAlpha()
A convenience method that gets the alpha (opacity) component of the
shape's color.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getAngularDamping()
Gets the angular damping of the shape, which is used to reduce the
angular velocity of the shape.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getAngularVelocity()
Gets the angular velocity of the shape, in degrees per second.
| ||||||||||
Body
|
getB2Body()
For advanced usage only.
| ||||||||||
BodyDef
|
getB2BodyDef()
For advanced usage only. | ||||||||||
abstract
RectF
|
getBounds()
Gets the bounding rectangle of the shape.
| ||||||||||
Color
|
getColor()
Gets the color of the receiver.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getDensity()
Gets the density of the shape.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getFriction()
Gets the coefficient of friction for the shape.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getGravityScale()
Gets the gravity scaling factory for this shape.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getHeight()
Gets the height of the shape, in pixels.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getLeft()
Gets the x-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding
box (the top-left corner, by default).
| ||||||||||
float
|
getLinearDamping()
Gets the linear damping of the shape, which is used to reduce the
linear velocity of the shape.
| ||||||||||
PointF
|
getLinearVelocity()
Gets the linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in
units per second.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getMass()
Gets the mass of this shape (which is the density of the shape multiplied by its surface area). | ||||||||||
final
ShapeView
|
getParentView()
Gets the parent of the receiver.
| ||||||||||
PointF
|
getPosition()
Gets the location of the centroid of the shape.
| ||||||||||
PointF
|
getPositionAnchor()
Get the current position anchor, which is an offset relative to the
upper left corner of the shape that is used as the shape's "origin"
for the purposes of getting/setting x-y positions.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getRestitution()
Gets the coefficient of restitution, which controls the "bounciness" of
the shape (or in more precise terms, the relationship between the
velocity of the shape before and after a collision).
| ||||||||||
float
|
getRotation()
Gets the current angle of rotation of the shape, in degrees clockwise.
| ||||||||||
final
ShapeField
|
getShapeField()
Gets the
ShapeField that contains this shape. | ||||||||||
ShapeMotion
|
getShapeMotion()
Gets a value indicating how this shape acts with regard to motion in
the physical world.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getTop()
Gets the y-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding
box (the top-left corner, by default).
| ||||||||||
Matrix
|
getTransform()
Gets the current linear transformation that will be applied to the
shape when it is drawn.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getWidth()
Gets the width of the shape, in pixels.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getX()
Gets the x-coordinate of the centroid of the shape.
| ||||||||||
float
|
getY()
Gets the y-coordinate of the centroid of the shape.
| ||||||||||
int
|
getZIndex()
Gets the z-index of the receiver.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
intersects(Shape otherShape)
Determine whether this shape intersects another, based on their
bounding boxes.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
isActive()
Gets a value indicating whether or not the shape is active.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
isAwake()
Gets a value indicating whether or not the shape is awake.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
isBullet()
Gets a value indicating whether this shape is a "bullet." Bullets are
very fast moving objects that require more precise contact/collision
handling than ordinary objects, and they require more processing power
as a result.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
isFixedRotation()
Gets a value indicating whether this shape's rotation is fixed -- that
is, even under a physical load, the shape will never rotate.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
isInFrontOf(Shape other)
Returns true if this shape is drawn in front of (later than) the
other shape.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
isSensor()
Gets a value indicating whether or not the shape is a sensor.
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
isVisible()
Gets a value indicating whether the receiver is visible (drawn on the
screen).
| ||||||||||
void
|
moveBy(float dx, float dy)
Moves the receiver by the specified horizontal and vertical distance.
| ||||||||||
void
|
remove()
Remove this shape from its view (or parent).
| ||||||||||
void
|
rotateBy(float angleDelta)
Increments the shape's rotation by the specified number of degrees,
around the same pivot point that was used previously (or the center
of the shape if no other pivot has been previously used).
| ||||||||||
void
|
setActive(boolean isActive)
Sets a value indicating whether or not the shape is active.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setAlpha(int newAlpha)
A convenience method that sets the alpha (opacity) component of the
shape's color without changing the other color components.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setAngularDamping(float newDamping)
Sets the angular damping of the shape, which is used to reduce the
angular velocity of the shape.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setAngularVelocity(float newVelocity)
Sets the angular velocity of the shape, in degrees per second.
| ||||||||||
abstract
void
|
setBounds(RectF newBounds)
Sets the bounding rectangle of the shape.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setBullet(boolean bullet)
Sets a value indicating whether this shape is a "bullet." Bullets are
very fast moving objects that require more precise contact/collision
handling than ordinary objects, and they require more processing power
as a result.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setColor(Color newColor)
Sets the color of the receiver.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setDensity(float newDensity)
Sets the density of the shape.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setFixedRotation(boolean fixedRotation)
Sets a value indicating whether this shape's rotation is fixed -- that
is, even under a physical load, the shape will never rotate.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setFriction(float newFriction)
Set the coefficient of friction for the shape.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setGravityScale(float gravityScale)
Sets the gravity scaling factor for the shape.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setLeft(float x)
Sets the x-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding
box (the top-left corner, by default).
| ||||||||||
void
|
setLinearDamping(float newDamping)
Sets the linear damping of the shape, which is used to reduce the
linear velocity of the shape.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setLinearVelocity(PointF newVelocity)
Sets the linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units
per second.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setLinearVelocity(float xVelocity, float yVelocity)
Sets the linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units
per second.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setPosition(float x, float y)
Sets the location of the centroid of the shape.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setPosition(PointF position)
Sets the location of the centroid of the shape.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setPositionAnchor(PointF anchor)
Set the position anchor, which is an offset relative to the
upper left corner of the shape that is used as the shape's "origin"
for the purposes of getting/setting x-y positions.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setRestitution(float newRestitution)
Sets the coefficient of restitution, which controls the "bounciness" of the shape (or in more precise terms, the relationship between the velocity of the shape before and after a collision). | ||||||||||
void
|
setRotation(float newRotation)
Sets the angle of rotation of the shape in degrees clockwise, using
the center of the shape's bounding box as the pivot point.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setSensor(boolean isSensor)
Gets a value indicating whether or not the shape is a sensor.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setShapeMotion(ShapeMotion motion)
Sets a value indicating how this shape acts with regard to motion in
the physical world.
| ||||||||||
void
|
setTop(float y)
Sets the y-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding
box (the top-left corner, by default).
| ||||||||||
void
|
setVisible(boolean newVisible)
Sets a value indicating whether the receiver is visible (drawn on the
screen).
| ||||||||||
void
|
setZIndex(int newZIndex)
Sets the z-index of the receiver.
| ||||||||||
void
|
stopAnimation()
Stops the current animation for this shape, if there is one.
| ||||||||||
String
|
toString()
Returns a human-readable string representation of the shape.
| ||||||||||
| Protected Methods | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
void
|
addFixtureForShape(org.jbox2d.collision.shapes.Shape b2Shape)
This method should only be called internally from within
#createFixtures(Body) in order to create fixtures for the shape
and add them to the shape's internal list of fixtures.
| ||||||||||
void
|
conditionallyRepaint()
Called to indicate that the shape needs to be repainted on the screen.
| ||||||||||
abstract
void
|
createFixtures()
This method is intended for internal use only, or by advanced
users subclassing one of the abstract shape types.
| ||||||||||
void
|
destroyFixtures()
Destroys the fixtures associated with this shape.
| ||||||||||
Paint
|
getPaint()
Gets the
Paint object that describes how this shape should be
drawn. | ||||||||||
float[]
|
inverseTransformPoint(float x, float y)
Transforms a point on the screen into the original bounds of a shape,
pre-rotation.
| ||||||||||
void
|
recreateFixtures()
Destroys and recreates the shape's fixtures.
| ||||||||||
void
|
updateTransform(float x, float y, float angle)
TODO document
| ||||||||||
void
|
updateTransform(float x, float y)
TODO document
| ||||||||||
void
|
updateTransform(float angle)
TODO document
| ||||||||||
Methods inherited from
class
java.lang.Object
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Object
|
clone()
| ||||||||||
boolean
|
equals(Object arg0)
| ||||||||||
void
|
finalize()
| ||||||||||
final
Class<?>
|
getClass()
| ||||||||||
int
|
hashCode()
| ||||||||||
final
void
|
notify()
| ||||||||||
final
void
|
notifyAll()
| ||||||||||
String
|
toString()
| ||||||||||
final
void
|
wait()
| ||||||||||
final
void
|
wait(long arg0, int arg1)
| ||||||||||
final
void
|
wait(long arg0)
| ||||||||||
Public Constructors
Creates a new shape.
Public Methods
Add another shape to the same view (or composite shape) containing this
shape. This method is a convenience shortcut for
getShapeParent().add(newShape), but with the added benefit that
it does nothing if the receiving shape is not added to a parent (and
thus the parent is null).
Parameters
- newShape
- The other shape to add.
Gets an animator object that lets the user animate properties of the receiving shape.
For ease of use, the description of the animation desired can be chained directly to the result of this method. For example, the following code fragment would create an animation that runs for 2 seconds, gradually changing the shape's color to red, its position to the top-right corner of the view, and then starts the animation after a delay of 1 second after the method is called:
shape.animate(2000)
.delay(1000)
.color(Color.red)
.position(Anchor.TOP_RIGHT.ofView())
.play();
Parameters
- duration
- The length of the animation in milliseconds.
Returns
A ShapeAnimator that lets the user animate properties of the receiving shape.
TODO document
Parameters
- x
- the magnitude of the impulse in the horizontal direction
- y
- the magnitude of the impulse in the vertical direction
Gets a value indicating whether the specified pixel location is contained in the receiver.
Parameters
- point
- The point.
Returns
True if the shape contains the point, otherwise false.
Gets a value indicating whether the specified pixel location is contained in the receiver.
By default, this method checks to see whether the point is located within the bounding rectangle of the shape. Shapes where this would produce incorrect results, such as ovals or lines, override this method accordingly.
This method does take the shape's rotation into
account. This means that if you subclass Shape and need to
provide logic that is different from the default bounding box behavior,
then you may need to undo the rotation of the incoming point before
testing it against your shape's bounds. The
inverseTransformPoint(float, float) method has been provided
to simplify this.
Parameters
- x
- The x-coordinate.
- y
- The y-coordinate.
Returns
True if the shape contains the point, otherwise false.
Subclasses must implement this method to define how the shape is to be
drawn on the canvas. Users should never call this method directly; it is
called as part of the repaint cycle by the ShapeView that
contains the shape.
Parameters
- canvas
- The Canvas on which to draw the shape.
Determine whether any part of this shape extends outside the given rectangle.
Parameters
- bounds
- The rectangle to check against.
Returns
A ViewEdges object indicating whether any part of this shape extends outside the top, bottom, left, or right side of the bounds.
A convenience method that gets the alpha (opacity) component of the shape's color.
Returns
The alpha component of the shape's color, where 0 means that the color is fully transparent and 255 means that it is fully opaque.
Gets the angular damping of the shape, which is used to reduce the angular velocity of the shape.
Returns
the angular damping of the shape
Gets the angular velocity of the shape, in degrees per second. (Note that this is different from JBox2D, which uses radians per second. We use degrees for consistency with the rest of the Android graphics subsystem.)
Returns
the angular velocity of the shape, in degrees per second
For advanced usage only. Gets the JBox2D
Body object that this shape represents.
Returns
the JBox2D Body object that this shape represents
For advanced usage only. Gets the JBox2D
BodyDef object that is used to create the rigid body represented
by this shape. A couple caveats:
- The JBox2D
Bodyis created when the shape is added to its parent (aShapeViewor CompositeShape), so changes to the returnedBodyDefwill only apply before that. - Do not modify the
userDataproperty of theBodyDefobject; it is used by Sofia to track theShapethat theBodyrepresents.
Returns
the JBox2D BodyDef object that this shape represents
Gets the bounding rectangle of the shape. The top-left corner of the bounding rectangle is the shape's origin, and the bottom-right corner is the shape's extent.
Returns
The bounding rectangle of the shape.
Gets the density of the shape. The mass of the shape is computed by multiplying the density of the shape by its surface area.
Returns
the density of the shape
Gets the coefficient of friction for the shape.
Returns
the coefficient of friction for the shape
Gets the gravity scaling factory for this shape.
Returns
the gravity scaling factor for the shape
Gets the height of the shape, in pixels.
Returns
The height of the shape.
Gets the x-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding box (the top-left corner, by default).
Returns
The x-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding box.
See Also
- #setPositionAnchor(Anchor)
Gets the linear damping of the shape, which is used to reduce the linear velocity of the shape.
Returns
the linear damping of the shape
Gets the linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units per second.
Returns
the linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units per second
Gets the mass of this shape (which is the density of the shape multiplied by its surface area).
This method can only be called on shapes that are currently added to a
ShapeField. If the shape is not in a field, this method will
throw an IllegalStateException.
Returns
the mass of this shape
Throws
- IllegalStateException
- if the shape is not currently in a field
Gets the parent of the receiver.
Returns
The parent of the receiver.
Gets the location of the centroid of the shape. Be aware that the PointF#x and PointF#y fields of the returned point may not be valid if layout of the shapes has not yet occurred.
Returns
A PointF object describing the location of the shape.
Get the current position anchor, which is an offset relative to the upper left corner of the shape that is used as the shape's "origin" for the purposes of getting/setting x-y positions. The default anchor is the top-left corner (0, 0) unless it has been explicitly set.
Returns
The current position anchor.
Gets the coefficient of restitution, which controls the "bounciness" of
the shape (or in more precise terms, the relationship between the
velocity of the shape before and after a collision). See
setRestitution(float) for ways to interpret this value.
Returns
the coefficient of restitution
Gets the current angle of rotation of the shape, in degrees clockwise.
Returns
The current angle of rotation of the shape.
Gets the ShapeField that contains this shape.
Returns
The ShapeField that contains this shape, or null if the
shape is not in a field.
Gets a value indicating how this shape acts with regard to motion in the physical world.
Returns
a ShapeMotion value indicating how this shape acts with
regard to motion in the physical world
See Also
Gets the y-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding box (the top-left corner, by default).
Returns
The y-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding box.
See Also
- #setPositionAnchor(Anchor)
Gets the current linear transformation that will be applied to the shape when it is drawn. Currently, the matrix only contains rotation information.
Returns
The current linear transformation that is applied to the shape.
Gets the width of the shape, in pixels.
Returns
The width of the shape.
Gets the x-coordinate of the centroid of the shape.
Returns
the x-coordinate of the centroid of the shape
Gets the y-coordinate of the centroid of the shape.
Returns
the y-coordinate of the centroid of the shape
Gets the z-index of the receiver. A shape with a higher z-index will be drawn on top of a shape with a lower z-index. Among shapes that have the same z-index, shapes added later will be drawn above shapes added earlier. By default, shapes are created with a z-index of 0.
Returns
The z-index of the shape.
Determine whether this shape intersects another, based on their bounding boxes.
Parameters
- otherShape
- The other shape to check against.
Returns
True if this shape and the other shape intersect.
Gets a value indicating whether or not the shape is active. Inactive shapes are drawn on the screen but do not report contact/collisions with other shapes.
Returns
true if the shape should be active and report contact/collision with other shapes; false if it should not
Gets a value indicating whether or not the shape is awake.
Returns
true if the shape is awake; false if it is asleep
Gets a value indicating whether this shape is a "bullet." Bullets are very fast moving objects that require more precise contact/collision handling than ordinary objects, and they require more processing power as a result.
Returns
true if this shape uses more precise "bullet" contact/collision handling, or false if it does not
Gets a value indicating whether this shape's rotation is fixed -- that is, even under a physical load, the shape will never rotate. This is can be useful for characters in games.
Returns
true if this shape has fixed rotation, or false if it is allowed to rotate
Returns true if this shape is drawn in front of (later than) the other shape.
Parameters
- other
- The shape to check against.
Returns
True if this shape is drawn in front of (later than) the other.
Gets a value indicating whether or not the shape is a sensor. Sensors are shapes that can be used to detect collisions, but they do not respond physically to those collisions.
Returns
true if the shape is a sensor; false if it is not
Gets a value indicating whether the receiver is visible (drawn on the screen). Invisible shapes also do not receive touch events.
Returns
True if the shape is visible, otherwise false.
Moves the receiver by the specified horizontal and vertical distance. Positive values move the shape to the right or down, and negative values move it to the left or up.
Parameters
- dx
- The number of pixels to move the shape horizontally.
- dy
- The number of pixels to move the shape vertically.
Remove this shape from its view (or parent).
Increments the shape's rotation by the specified number of degrees, around the same pivot point that was used previously (or the center of the shape if no other pivot has been previously used).
Parameters
- angleDelta
- The number of degrees to add to the shape's rotation.
Sets a value indicating whether or not the shape is active. Inactive shapes are drawn on the screen but do not report contact/collisions with other shapes.
Parameters
- isActive
- true if the shape should be active and report contact/collision with other shapes; false if it should not
A convenience method that sets the alpha (opacity) component of the shape's color without changing the other color components.
Parameters
- newAlpha
- The new alpha component of the shape's color, where 0 means that the color is fully transparent and 255 means that it is fully opaque.
Sets the angular damping of the shape, which is used to reduce the
angular velocity of the shape. This can be a value between 0.0f
(no damping) and POSITIVE_INFINITY (full damping).
Parameters
- newDamping
- the angular damping of the shape
Sets the angular velocity of the shape, in degrees per second. (Note that this is different from JBox2D, which uses radians per second. We use degrees for consistency with the rest of the Android graphics subsystem.)
Parameters
- newVelocity
- the angular velocity of the shape, in degrees per second
Sets the bounding rectangle of the shape. The bounding rectangle passed to this method is copied, so changes to it after this method is called will not be reflected by the shape.
Parameters
- newBounds
- The new bounding rectangle of the shape.
Sets a value indicating whether this shape is a "bullet." Bullets are very fast moving objects that require more precise contact/collision handling than ordinary objects, and they require more processing power as a result.
Parameters
- bullet
- true if this shape uses more precise "bullet" contact/collision handling, or false if it does not
Sets the color of the receiver.
Parameters
- newColor
- The new color of the receiver.
Sets the density of the shape. The mass of the shape is computed by multiplying the density of the shape by its surface area.
Parameters
- newDensity
- the density of the shape
Sets a value indicating whether this shape's rotation is fixed -- that is, even under a physical load, the shape will never rotate. This is can be useful for characters in games.
Parameters
- fixedRotation
- true if this shape has fixed rotation, or false if it is allowed to rotate
Set the coefficient of friction for the shape.
Parameters
- newFriction
- the coefficient of friction for the shape
Sets the gravity scaling factor for the shape. This can be used to create interesting gravitational effects for individual shapes; for example, setting it to 0.0 would cause the shape to float in mid-air.
Parameters
- gravityScale
- the desired gravity scaling factor for the shape
Sets the x-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding box (the top-left corner, by default). This moves the shape, so calling this method also causes the extent of the shape to change, keeping with width the same.
Parameters
- x
- The x-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding box.
See Also
- #setPositionAnchor(Anchor)
Sets the linear damping of the shape, which is used to reduce the
linear velocity of the shape. This can be a value between 0.0f
(no damping) and POSITIVE_INFINITY (full damping).
Parameters
- newDamping
- the linear damping of the shape
Sets the linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units per second.
Parameters
- newVelocity
- the linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units per second
Sets the linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units per second.
Parameters
- xVelocity
- the horizontal linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units per second
- yVelocity
- the vertical linear velocity of the center of mass of the shape, in units per second
Sets the location of the centroid of the shape.
Parameters
- x
- the x-coordinate of the desired centroid of the shape
- y
- the y-coordinate of the desired centroid of the shape
Sets the location of the centroid of the shape.
Parameters
- position
- A PointF object describing the centroid of the shape.
Set the position anchor, which is an offset relative to the upper left corner of the shape that is used as the shape's "origin" for the purposes of getting/setting x-y positions. This does not change the shape's current position, but will change the behavior of future calls to setX()/setY()/setPosition() and getX()/getY()/getPosition().
Parameters
- anchor
- The new position anchor.
Sets the coefficient of restitution, which controls the "bounciness" of the shape (or in more precise terms, the relationship between the velocity of the shape before and after a collision).
A coefficient of restitution of 0 indicates that the object should effectively "stop" at the point of impact (that is, it will lose all velocity but may still remain in motion due to gravitational effects), while a coefficient of restitution of 1 indicates that the shape's velocity should have the same velocity after the impact as it did before. Coefficients of restitution greater than 1 are also possible; an example would be an object triggering an explosion upon impact and being blasted away.
The physics engine underlying Sofia Graphics does not support negative coefficients of restitution.
Details
Imagine that you have an object being dropped from a height of H and you want to compute the coefficient of restitution that will cause it to reach a height of h after it bounces. This can be computed using the following formula:
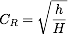 .
.
Similarly, if you have an object traveling at velocity u and you want it to have velocity v after the impact, you can compute the desired restitution with the formula:
 .
.
When two objects in motion collide, the maximum coefficient of restitution of the two objects is used to compute the new velocities after impact. This coefficient is defined to be
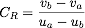 .
.
Finally, the velocities of the objects after a collision can be computed as follows:
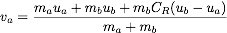 and
and
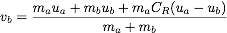 ,
,
where va and vb are the velocities of the objects after impact, ua and ub are the velocities before impact, and ma and mb are the masses of the objects.
Parameters
- newRestitution
- the new coefficient of restitution
Sets the angle of rotation of the shape in degrees clockwise, using the center of the shape's bounding box as the pivot point.
Parameters
- newRotation
- The new angle of rotation of the shape.
Gets a value indicating whether or not the shape is a sensor. Sensors are shapes that can be used to detect collisions, but they do not respond physically to those collisions.
Parameters
- isSensor
- true if the shape is a sensor; false if it is not
Sets a value indicating how this shape acts with regard to motion in the physical world.
Parameters
- motion
- a
ShapeMotionvalue indicating how this shape acts with regard to motion in the physical world
See Also
Sets the y-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding box (the top-left corner, by default). This moves the shape, so calling this method also causes the extent of the shape to change, keeping with height the same.
Parameters
- y
- The y-coordinate of the anchor point of the shape's bounding box.
See Also
- #setPositionAnchor(Anchor)
Sets a value indicating whether the receiver is visible (drawn on the screen).
Parameters
- newVisible
- True if the shape should be visible, otherwise false.
Sets the z-index of the receiver.
Parameters
- newZIndex
- The new z-index of the shape.
Stops the current animation for this shape, if there is one.
Returns a human-readable string representation of the shape.
Returns
A human-readable string representation of the shape.
Protected Methods
This method should only be called internally from within #createFixtures(Body) in order to create fixtures for the shape and add them to the shape's internal list of fixtures.
Parameters
- b2Shape
- a JBox2D shape that represents part or all of this shape
Called to indicate that the shape needs to be repainted on the screen. Most users will not need to call this method, because modifying a property of the shape such as its color will repaint it automatically.
This method is intended for internal use only, or by advanced
users subclassing one of the abstract shape types. Subclasses
must override this method to create the necessary fixtures for the body
that this shape represents. Use the getB2Body() method to access
the body when creating fixtures.
Destroys the fixtures associated with this shape. Most subclasses will
not need to call this method directly; instead, they should call
recreateFixtures() when the shape changes in a way that
requires its fixtures to be recreated (such as when its size changes).
Gets the Paint object that describes how this shape should be
drawn. By default, the Paint's style is set to STROKE
and the color to the value returned by getColor(). Subclasses
can override this method to add their own attributes; they should call
the superclass implementation and then add their own styles to the
returned object.
Returns
A Paint object describing how the shape should be drawn.
Transforms a point on the screen into the original bounds of a shape,
pre-rotation. This method is mainly meant to be used by subclasses
that need to provide their own contains(float, float)
implementation, so that those methods return the correct values when
a rotation is applied to the shape.
Parameters
- x
- The x-coordinate in the view.
- y
- The y-coordinate in the view.
Returns
A two-element float array that contains the x- and y-coordinates that the inputs would map to before the rotation was applied.
Destroys and recreates the shape's fixtures. Subclasses should call this method when a property of the shape changes that require its fixtures to be recreated, such as when its size changes.
TODO document
Parameters
- x
- the x-coordinate of the position of the centroid of the shape
- y
- the y-coordinate of the position of the centroid of the shape
- angle
- the rotation angle, in radians (note that this is different from the public interface, which uses degrees)
TODO document
Parameters
- x
- the x-coordinate of the position of the centroid of the shape
- y
- the y-coordinate of the position of the centroid of the shape
TODO document
Parameters
- angle
- the rotation angle, in radians (note that this is different from the public interface, which uses degrees)